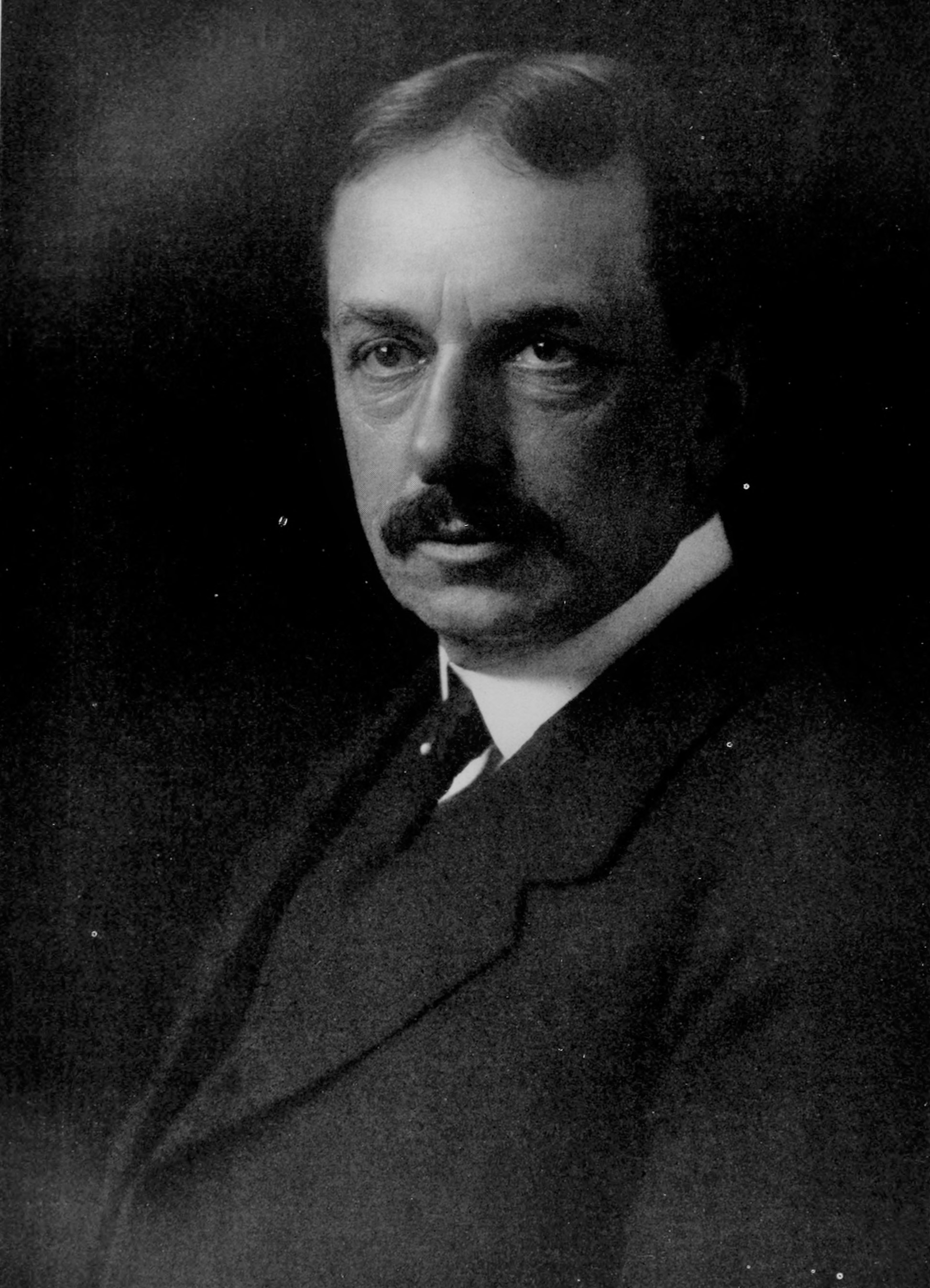
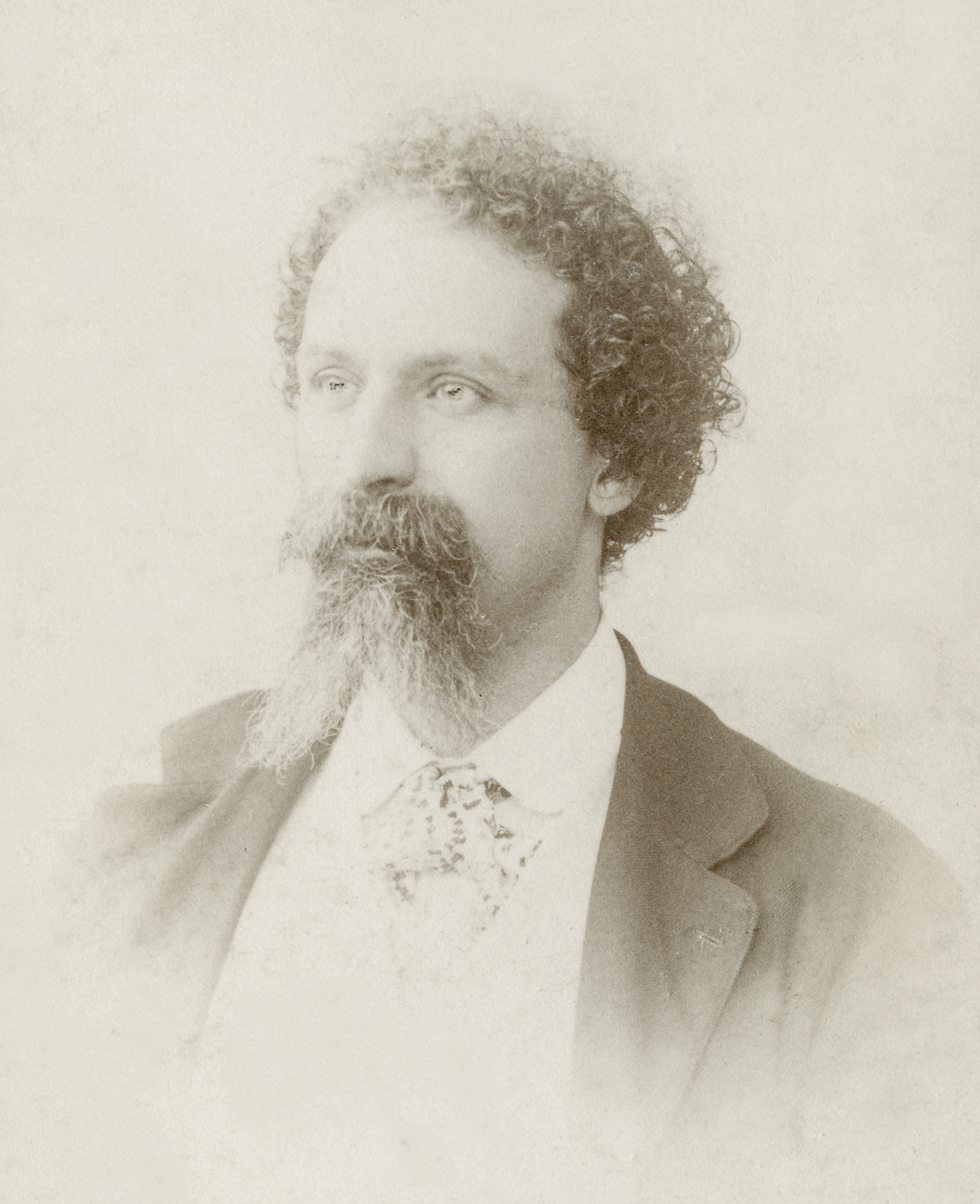
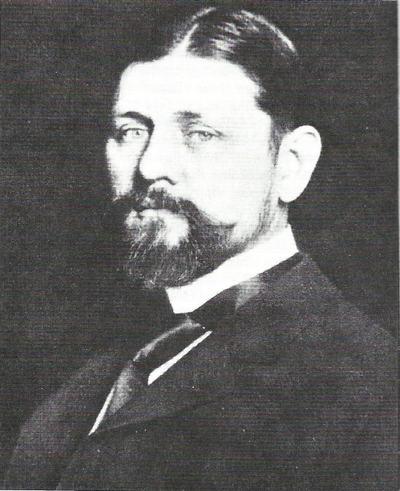
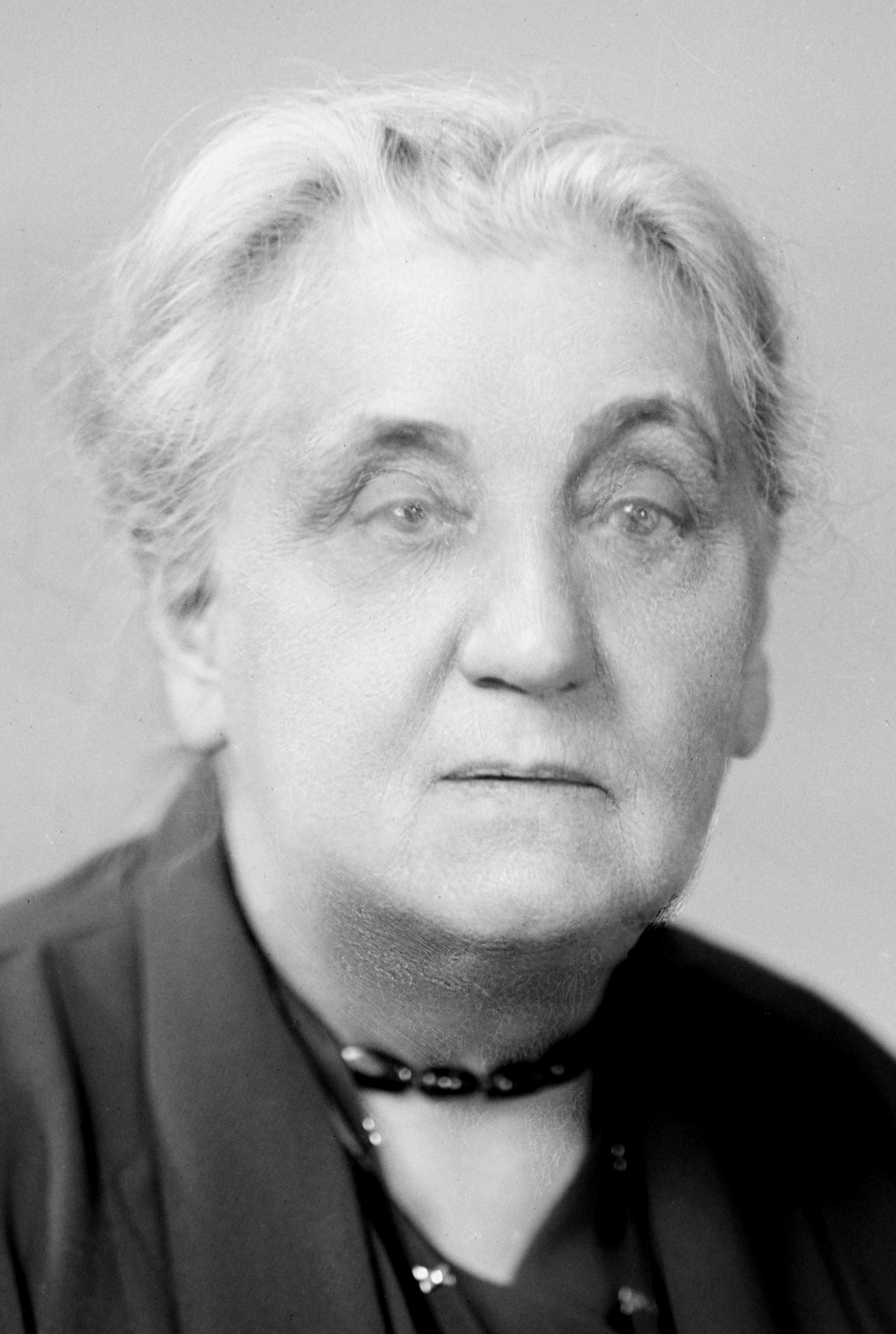
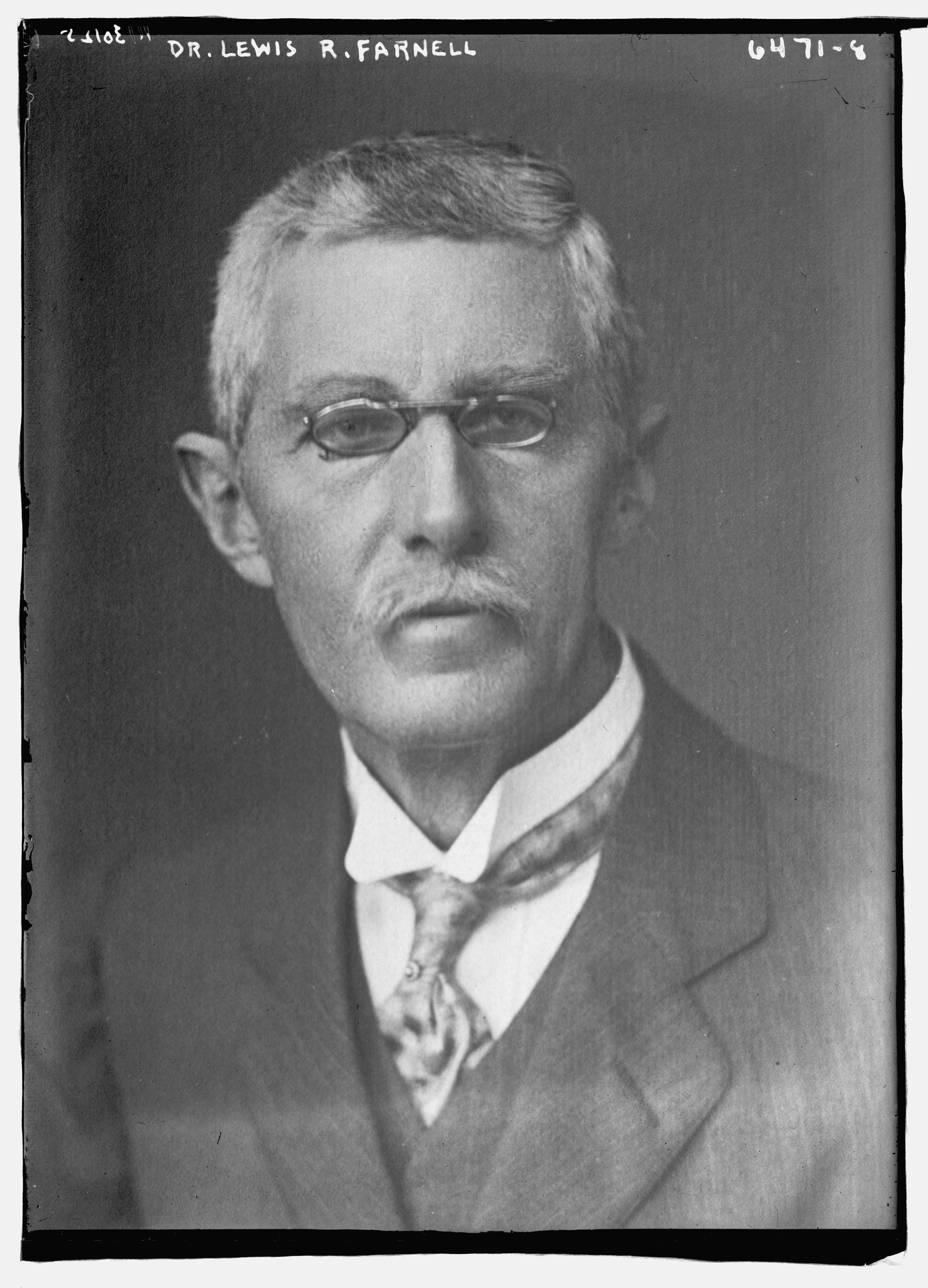
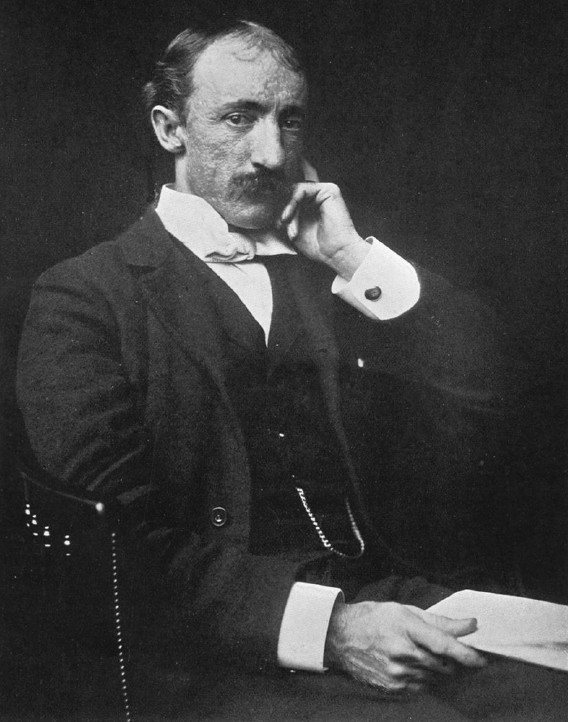Franz Boas
Franz Uri Boas (July 9, 1858 – December 21, 1942) was a German-American anthropologist and ethnomusicologist. He was a pioneer of modern anthropology who has been called the "Father of American Anthropology". His work is associated with the movements known as historical particularism and cultural relativism. Studying in Germany, Boas was awarded a doctorate in 1881 in physics while also studying geography. He then participated in a geographical expedition to northern Canada, where he became fascinated with the culture and language of the Baffin Island Inuit. He went on to do field work with the indigenous cultures and languages of the Pacific Northwest. In 1887 he emigrated to the United States, where he first worked as a museum curator at the Smithsonian, and in 1899 became a professor of anthropology at Columbia University, where he remained for the rest of his career. Through his students, many of whom went on to found anthropology departments and research programmes inspired by their mentor, Boas profoundly influenced the development of American anthropology. Among his many significant students were A. L. Kroeber, Alexander Goldenweiser, Ruth Benedict, Edward Sapir, Margaret Mead, Zora Neale Hurston, and Gilberto Freyre. Boas was one of the most prominent opponents of the then-popular ideologies of scientific racism, the idea that race is a biological concept and that human behavior is best understood through the typology of biological characteristics. In a series of groundbreaking studies of skeletal anatomy, he showed that cranial shape and size was highly malleable depending on environmental factors such as health and nutrition, in contrast to the claims by racial anthropologists of the day that held head shape to be a stable racial trait. Boas also worked to demonstrate that differences in human behavior are not primarily determined by innate biological dispositions but are largely the result of cultural differences acquired through social learning. In this way, Boas posed culture as the primary concept for describing differences in behavior between human groups, and as the central analytical concept of anthropology.
Famous Quotes
View all 3 quotes“The passion for seeking the truth for truth's sake...can be kept alive only if we continue to seek the truth for truth's sake.”
“It would seem that mythological worlds have been built up only to be shattered again, and that new worlds were built from the fragments.”
“I believe the present state of our knowledge justifies us in saying that, while individuals differ, biological differences are small. There is no reason to believe that one race is by nature so much more intelligent, endowed with great will power, or emotionally more stable than another that the difference would materially influence its culture.”


![Anthropology: [A Lecture Delivered At Columbia University In The Series On Science, Philosophy And Art, December 18, 1907]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd3b2n8gj62qnwr.cloudfront.net%2FCOVERS%2Fgutenberg_covers75k%2Febook-74049.png&w=3840&q=75)